3D Printing Surgical Guide
With the everyday increases in dental implant demand, the standard dental care requires a guided surgery for implant placement to have better predictability and accuracy while reducing the risks to ultimately provide a better patient experience with more successful procedures. Today, it is very easy and accessible to digitally plan implant placement by using a CT scan and intraoral scan of the jaws, designing a Surgical Guide in a dental implant CAD software, and finally fabricating the surgical guide by using a biocompatible resin in a SprintRay 3D printer.
Here we show and walk you through every step involved in the workflow of fabricating a Surgical Guide in your office, from impression taking to completing the appliance.
What you need: Designing is done on an Implant Planning software, which can be done in house or through a service provider.

What you need: Surgical Guide Sleeve, Muslin, Pumice, Nitrile gloves, Protective eyewear.
Digital Impression
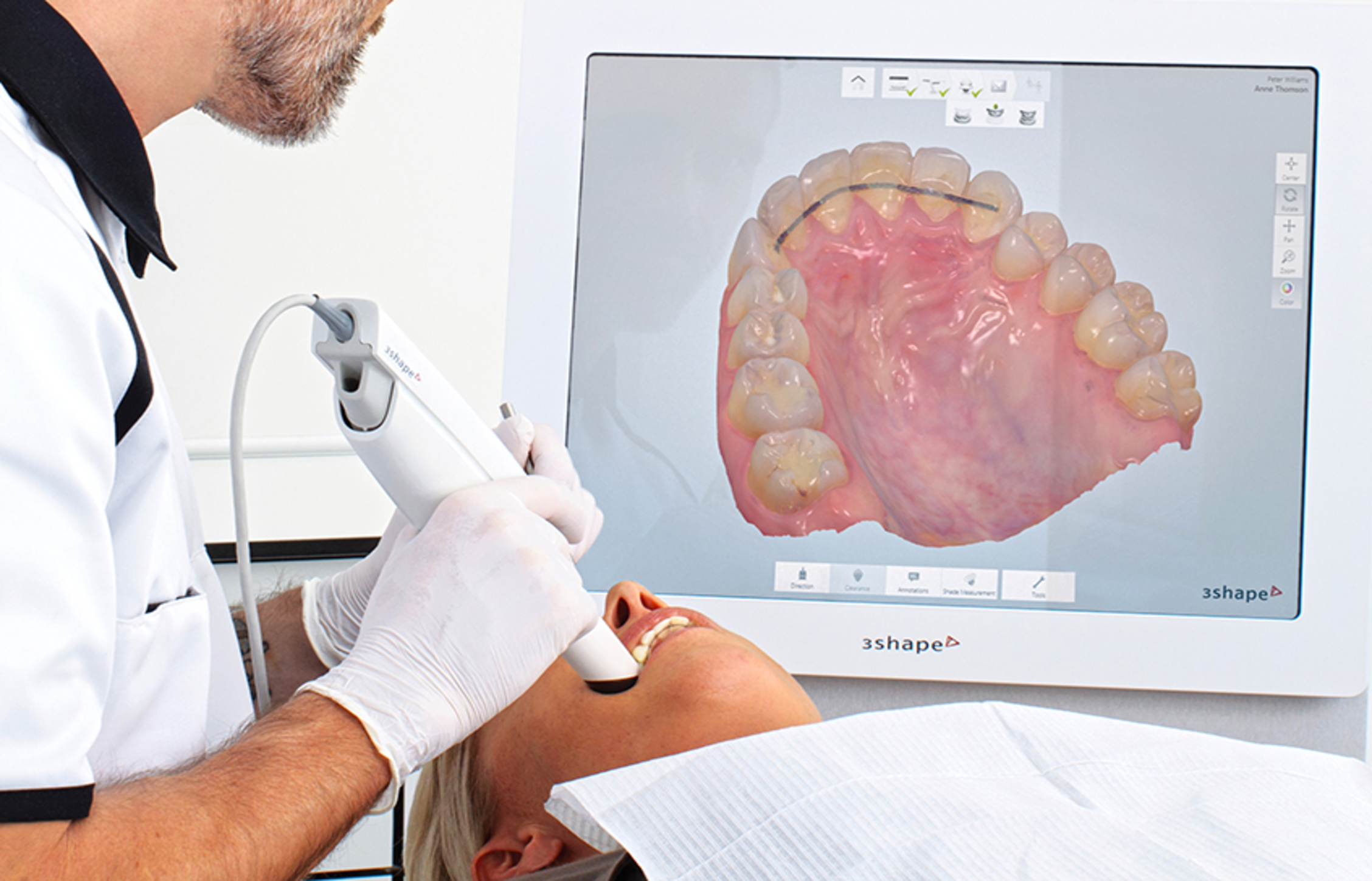
The first step in this workflow is to obtain CBCT data and digitally record a patient’s dentition information by a digital impression for being able to design the Surgical Guide in CAD software. We can either take a direct or indirect digital impressions.
Time required: 5-10 min
1.1. Using Intraoral Scanner
Use an intraoral scanner to take direct digital impressions, then export STL files. Common compatible scanners include, but are not limited to: Primescan (DentsplySirona), iTero (Align Tech), Trios (3Shape), Omnicam (DentsplySirona), Emerald (Planmeca), Medit (Medit), CS3700 (Carestream).

1.2. Using Desktop Scanner
Indirect digital impressions are done by using a desktop scanner to convert a VPS impression or a model into a digital impression. Once the maxillary, mandibular, and bite scan files (digital impressions) are ready, export and save them in the highest resolution (if you have the option of choosing resolution) on your computer in STL format.

Pro Tips
- Primescan does not allow exporting bite-scan as a separate file. By default, Primescan users can only export 2 files: upper and lower. In case you need to export bite-scan as a separate file, you need to follow the steps from this link: Link to “How to export separate bite-scan file from Primescan”
- To avoid rescanning and delays to the workflow, make sure all critical and required areas are scanned and captured. This will mitigate any delays in the treatment and discomfort to the patient. Here are some examples of problematic scans:
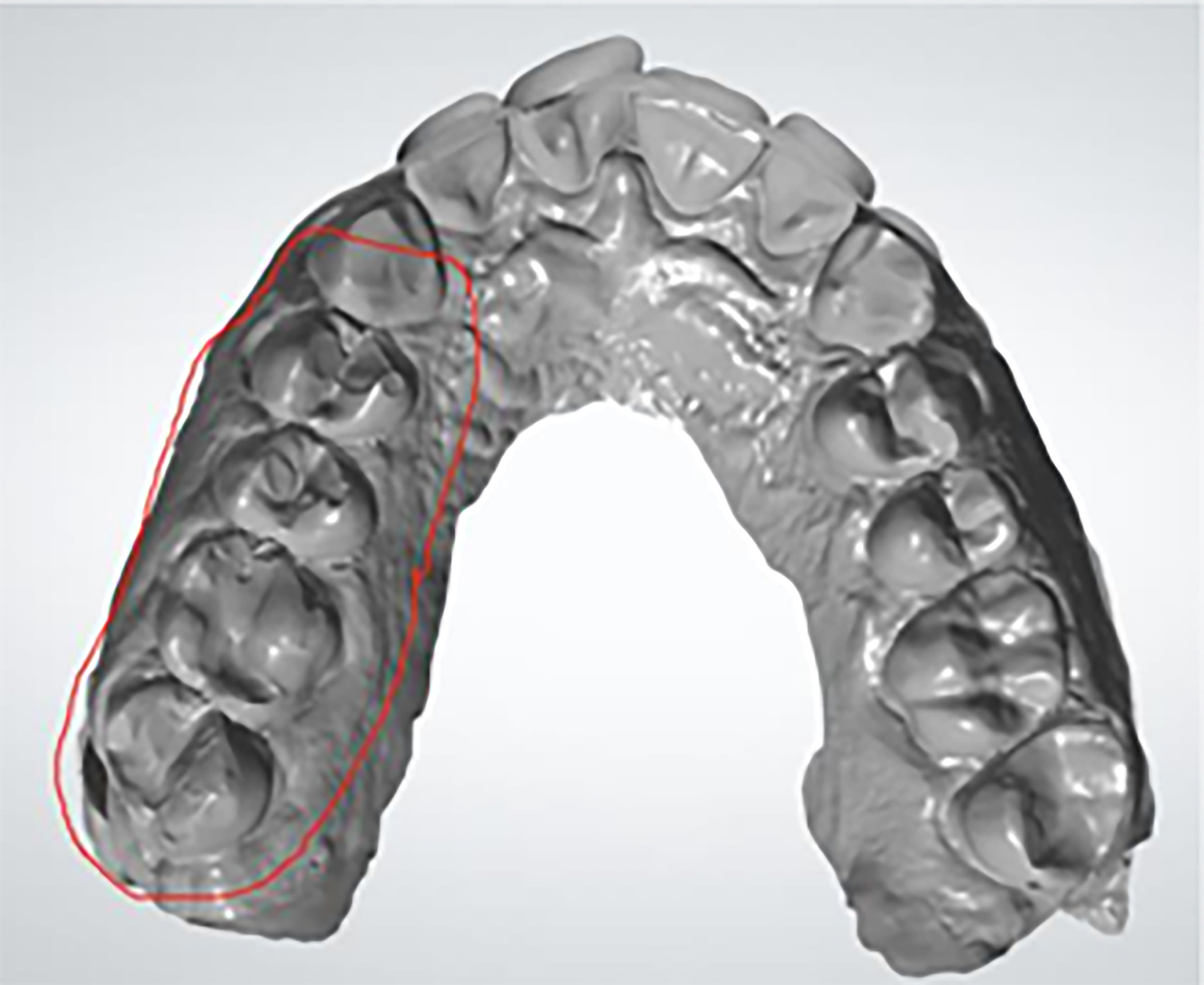
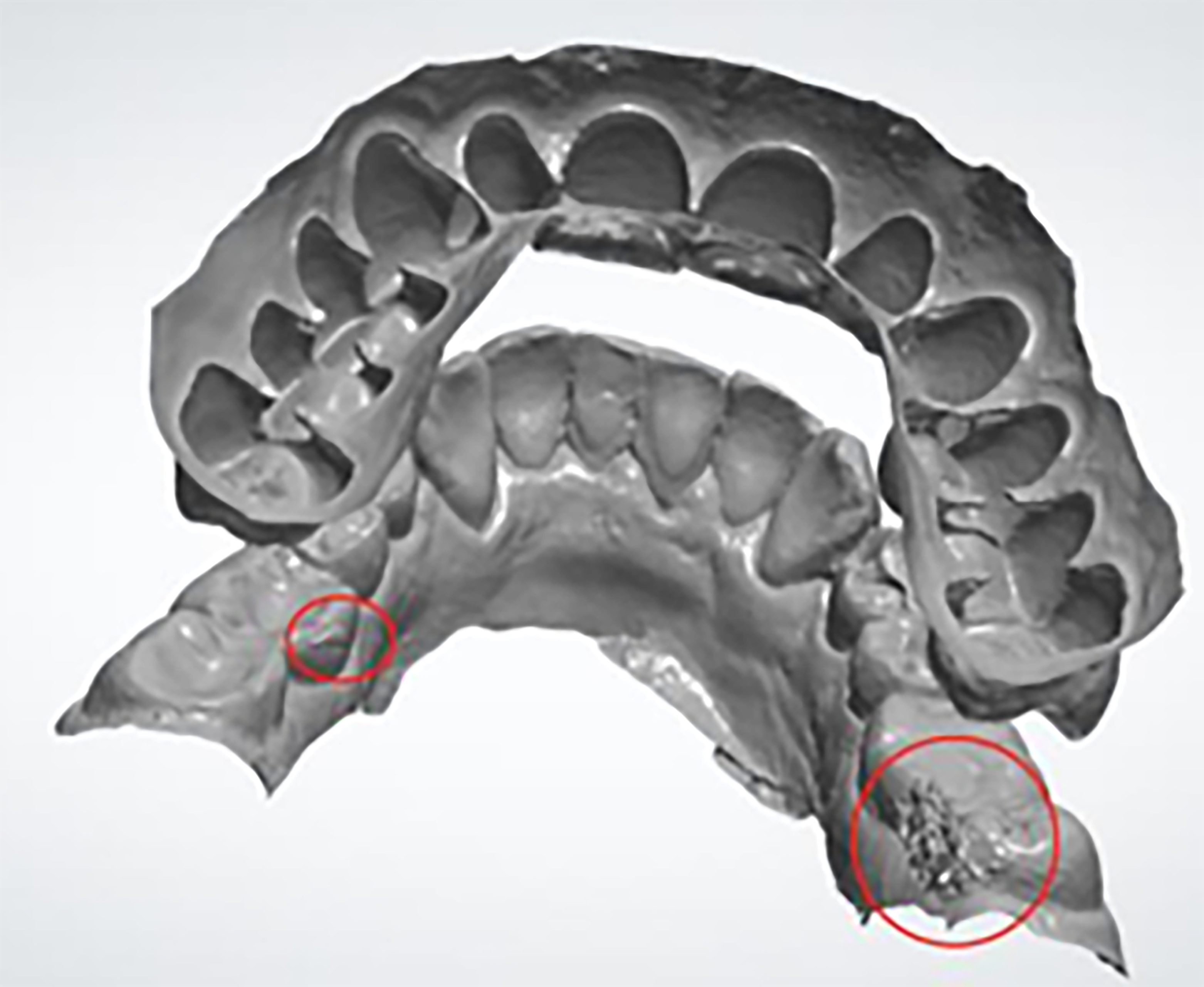
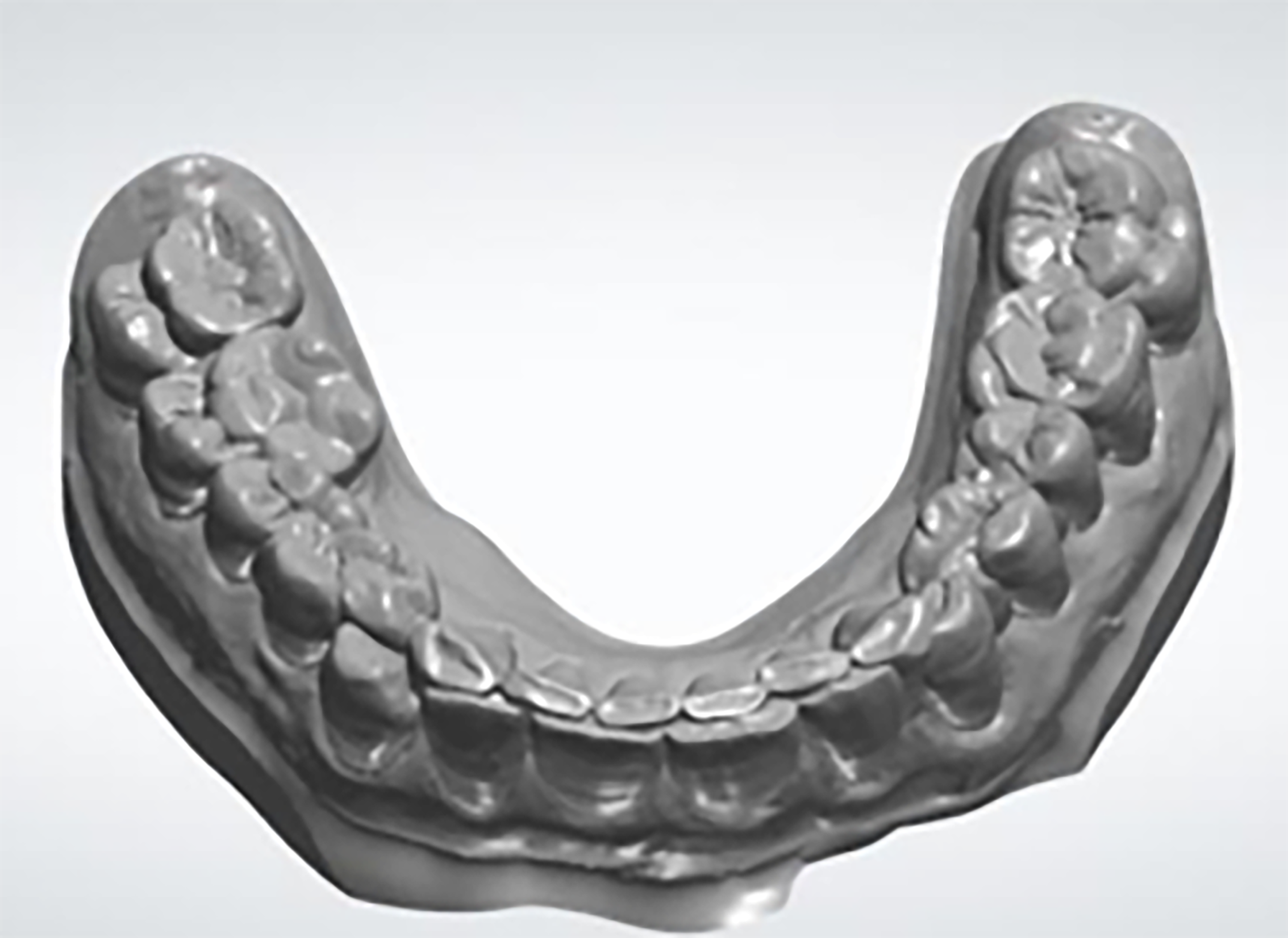
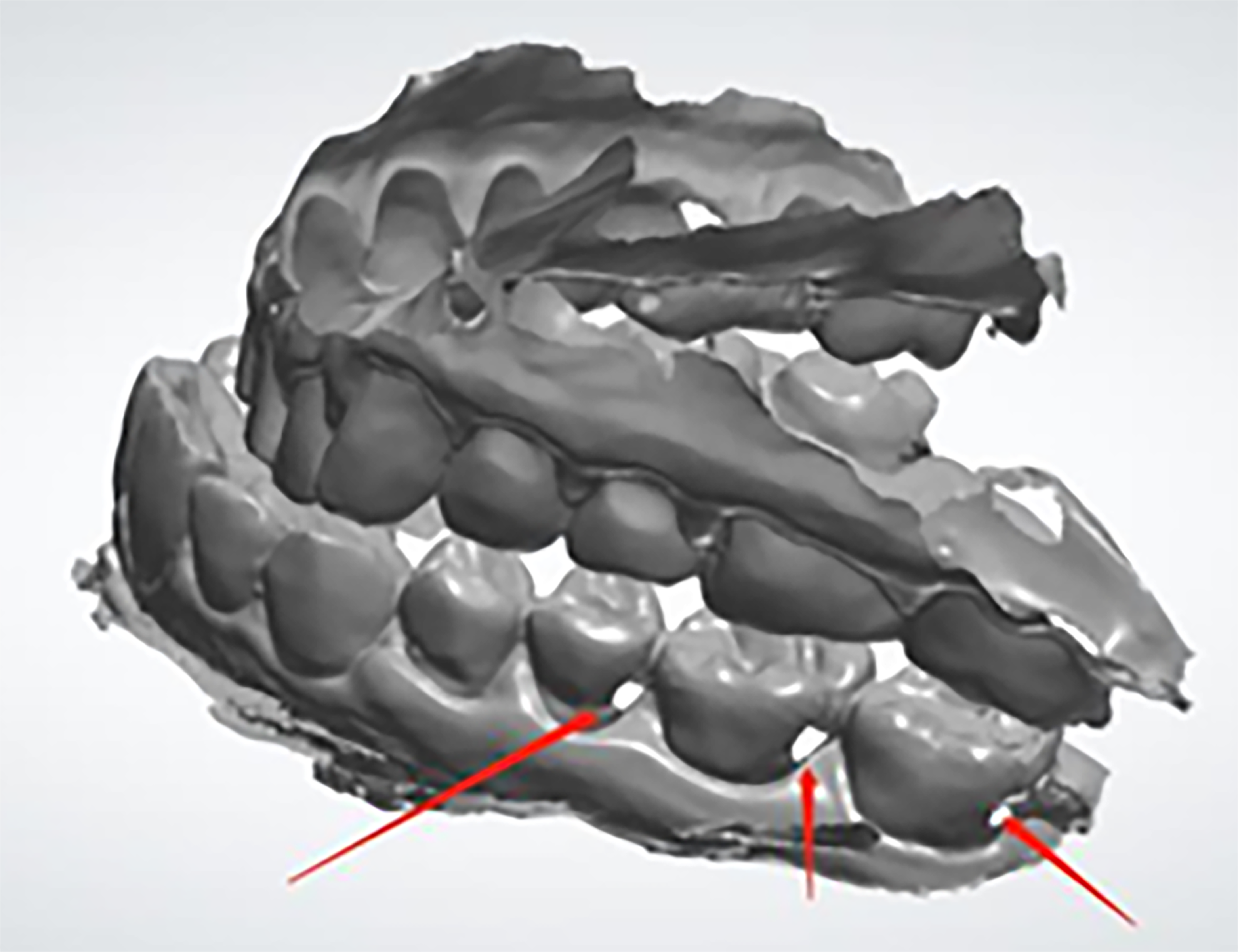
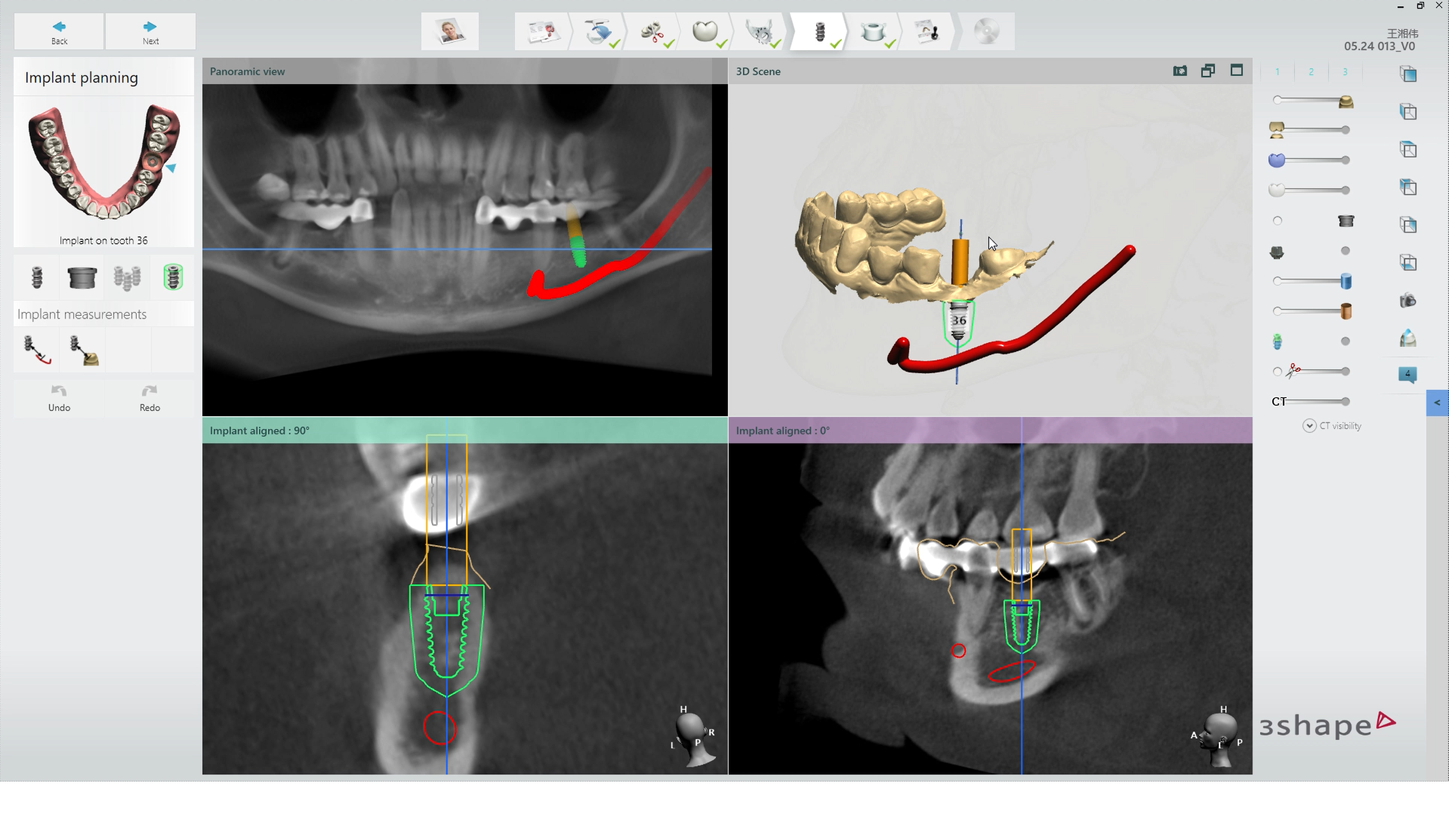
Surgical Guide Design
Designing the Surgical Guide is the second step in this workflow. Designing can be done either by using an outside provider, or it may be done in-house by the dentist.
Time required, if done in-office: 12-20 min.
2.1. Out of Office Surgical Guide Design
SprintRay Cloud Design helps and provides accurate Implant Planning and high-quality Surgical Guide Design, where you can upload patient's intraoral scan files, CBCT images, and your prescription. Click here for more information on SprintRay Cloud Design services: SprintRay Cloud Design. This process is done in 2 steps: first, you receive a link to a set of validated information regarding the implant planning guide design (such as a video summary, STL files, quality control images, and PDF files). Once the implant planning is approved, you will be sent the actual design file for the Surgical Guide. Once you receive the STL file of the designed Surgical Guide from SprintRay Cloud Design, you may go directly to step 3 (Fabricating Surgical Guide)

2.2. In-Office Designing Surgical Guide Design
This is done in a Splint CAD software. SprintRay Software allows you to choose a splint software that best meets your clinical needs. Below is the list showing our recommended options, however, our software accepts any design file formatted in STL, which means you can use whichever software you are most comfortable with: 3Shape Splint Studio, Exocad, Magics, D3splint. Once the scans are imported to the design software:

2.2.1. Proper Software Settings Required
Follow the instructions for SprintRay Surgical Guide material and choose/provide proper settings in the software. Continue to complete the implant planning followed by designing a Surgical Guide.
2.2.2. Export Designs as STL
Once Surgical Guide is designed, the appliance should be exported and saved in STL format.
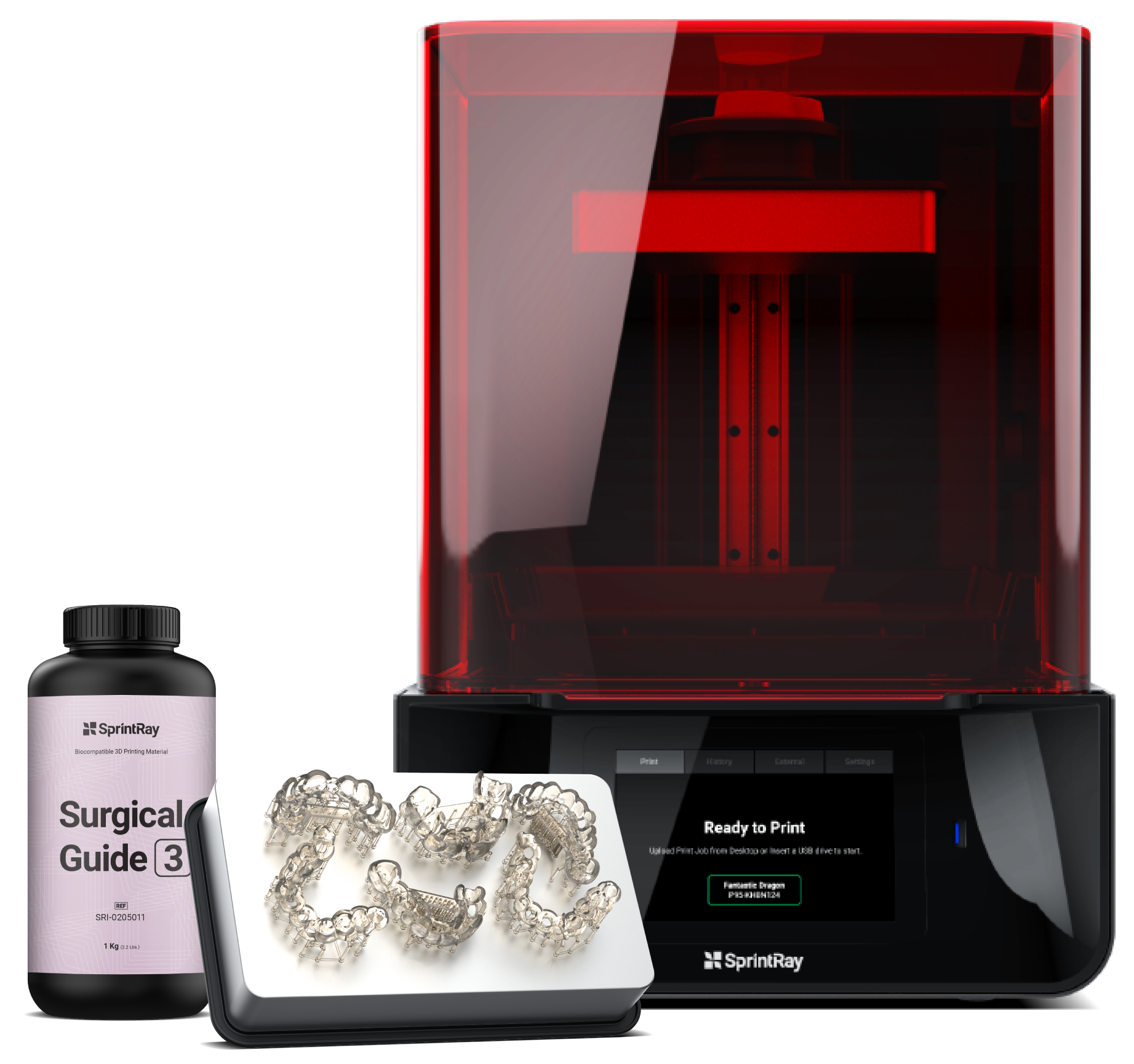
Surgical Guide Fabrication
Fabricating the Surgical Guide is the third step in this workflow. Once the design of the appliance is ready, you may start printing it using RayWare software and a SprintRay Pro printer. Below, we will show you the steps involved in fabricating the Surgical Guide.
If you use SprintRay Cloud Design services to design the Surgical Guide, you may use the direct print option. Click on the “Print” button and send the design directly to the printer. In this case, you may jump to step 3.5, otherwise, continue with step 3.1. Click here to learn more about direct print option and workflow on SprintRay Cloud Design services: SprintRay Cloud Design
Time required: 75-120 minutes
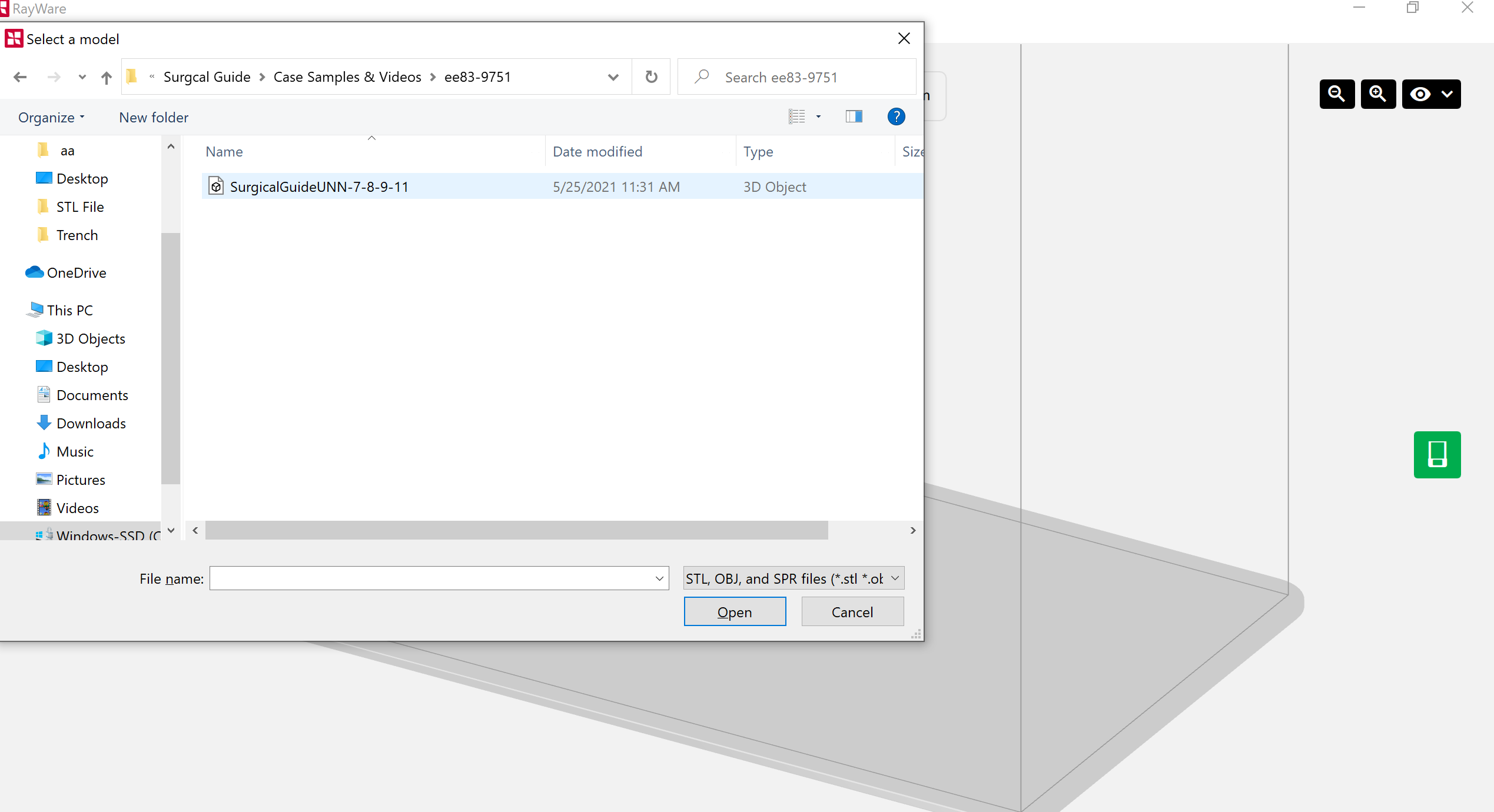
3.1. Initial Preparation
To prepare the appliance design for printing, import it to RayWare in STL format.
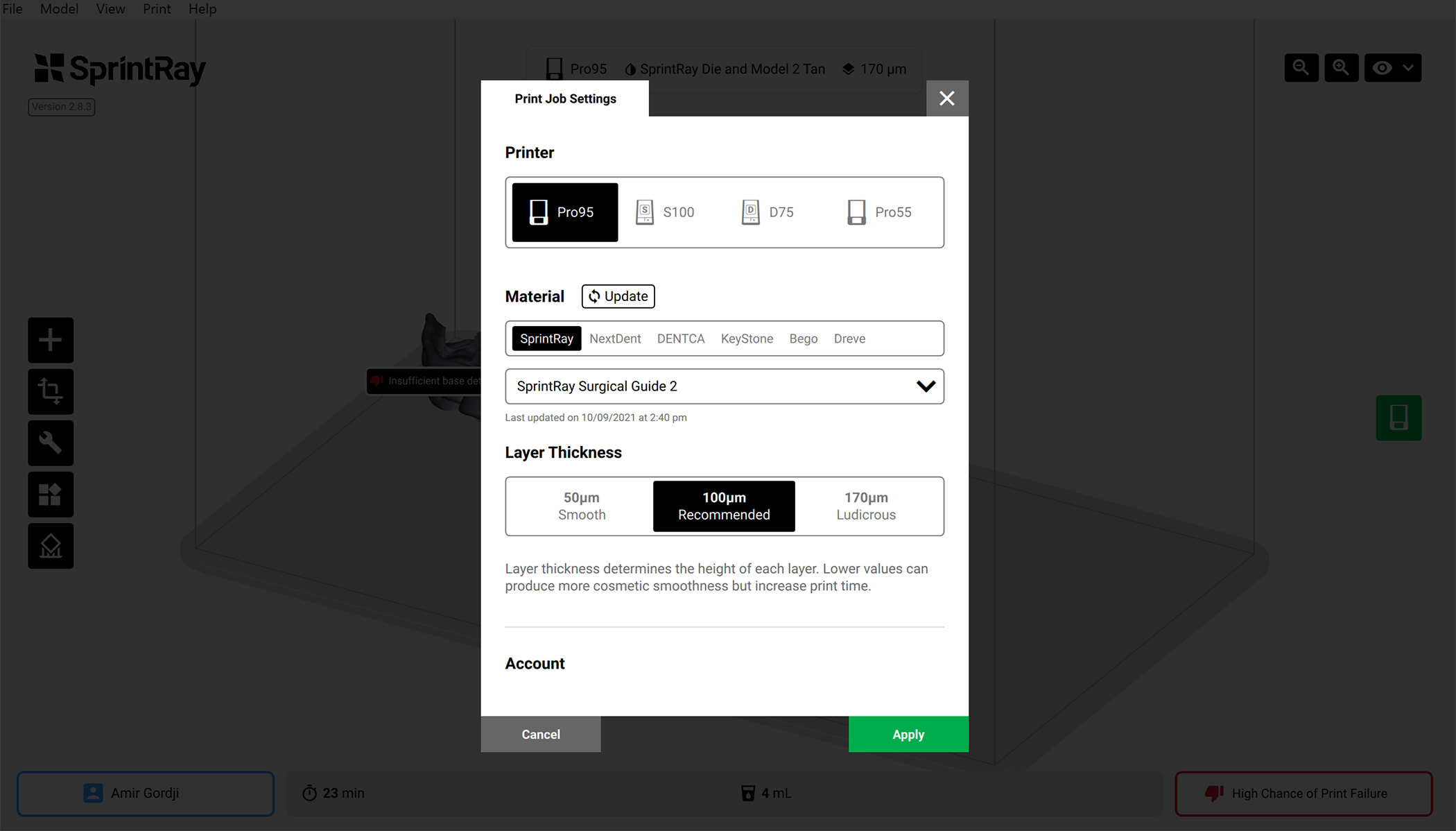
3.2. Print Settings and Configuration
The recommended resin for printing the Surgical Guide is SprintRay Surgical Guide 2, and the recommended thickness is 100 microns. This thickness provides great accuracy for surgical guide fabrication.
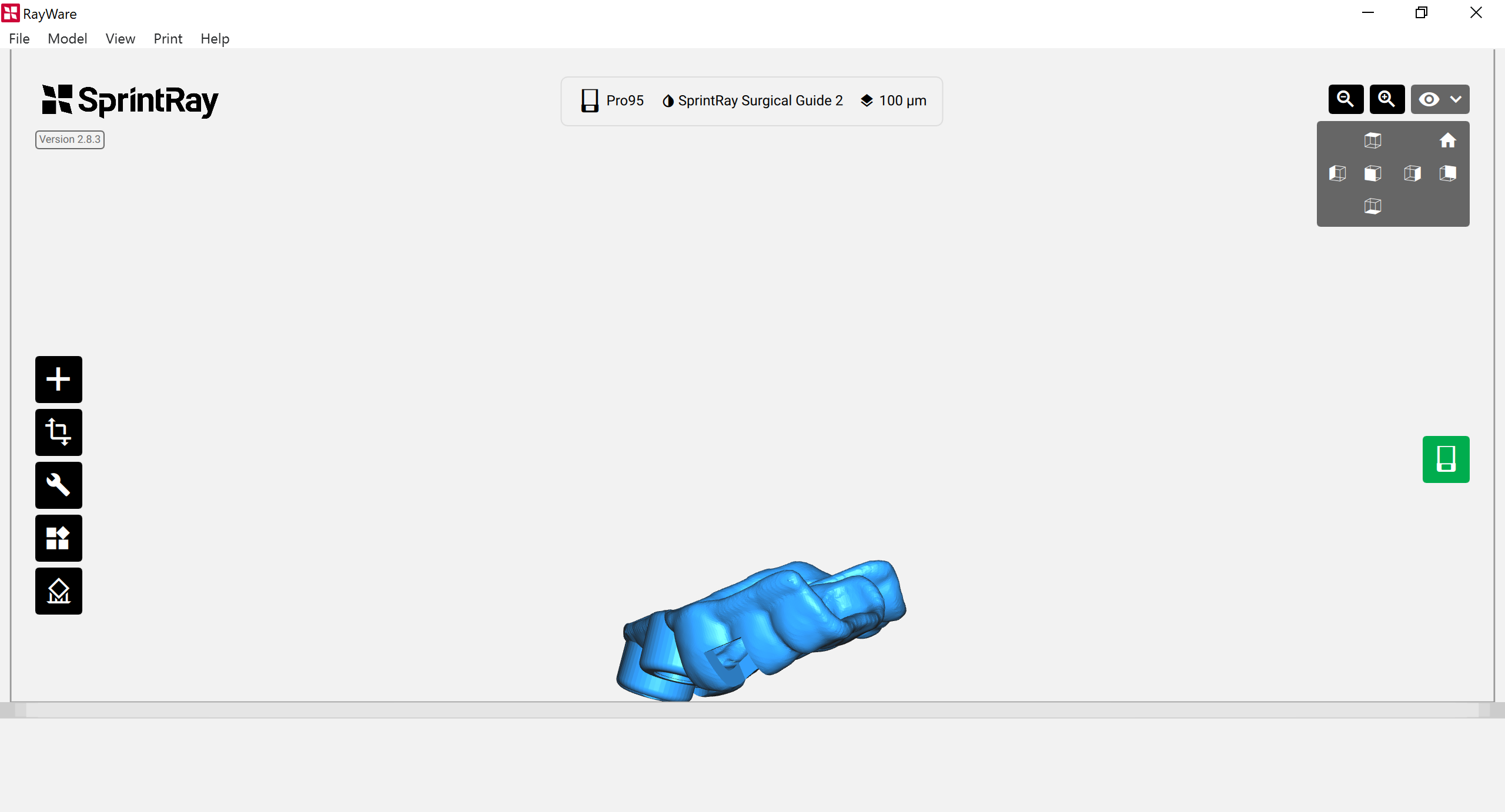
3.3. Print Orientation
The print orientation/angulation is an important printing factor. We recommend the following for best results:
- The intaglio surface should be facing up.
- The occlusal plane should be at an angle of 20-30 degrees to the print platform.
- The anterior part of the design should be closer to the print platform than the posterior.

3.4. Adding Supports
Once the orientation is obtained, the supports should be added to the design using the “Supports” button on the left side of the screen. We highly recommend printing the design with full supports to avoid any inaccuracies in the final product. Using supports only in the anterior region may lead to a lack of fitment. Make sure there is no support attachment within the drill holes or at the edge of them.
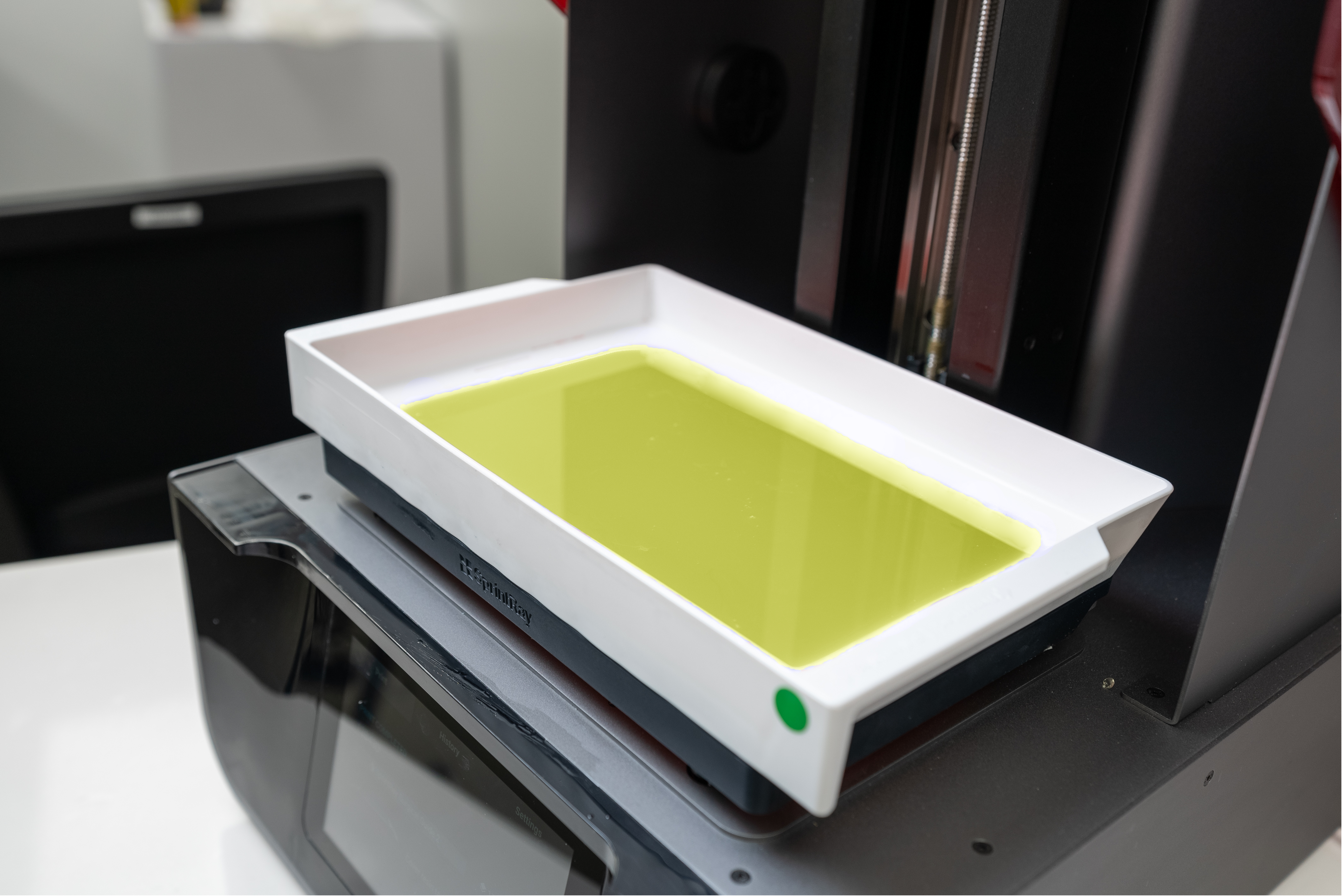
3.5. Prepare 3D printer and set print settings
Once settings are complete, check the resin level in the resin tank. It should stand between the minimum and maximum lines. If there is leftover resin in the tank from the previous print, use the provided resin wiper to stir the resin before printing. This ensures that the resin is properly mixed and clean. Make sure the resin tank is fully secured in place.
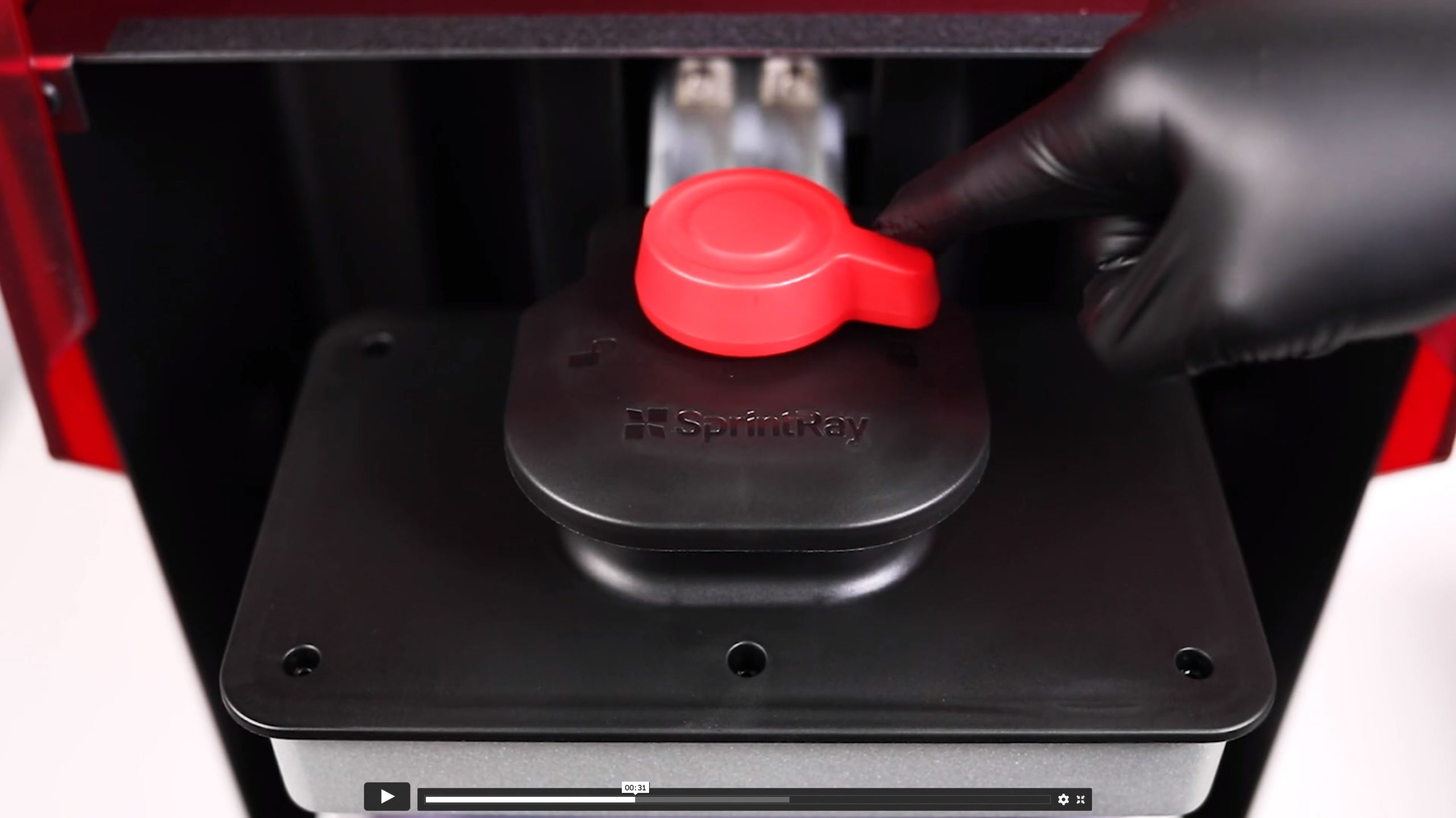

3.5.1. Platform check
Make sure the print platform is clean, dry, and securely placed, and locked on the platform-arm.
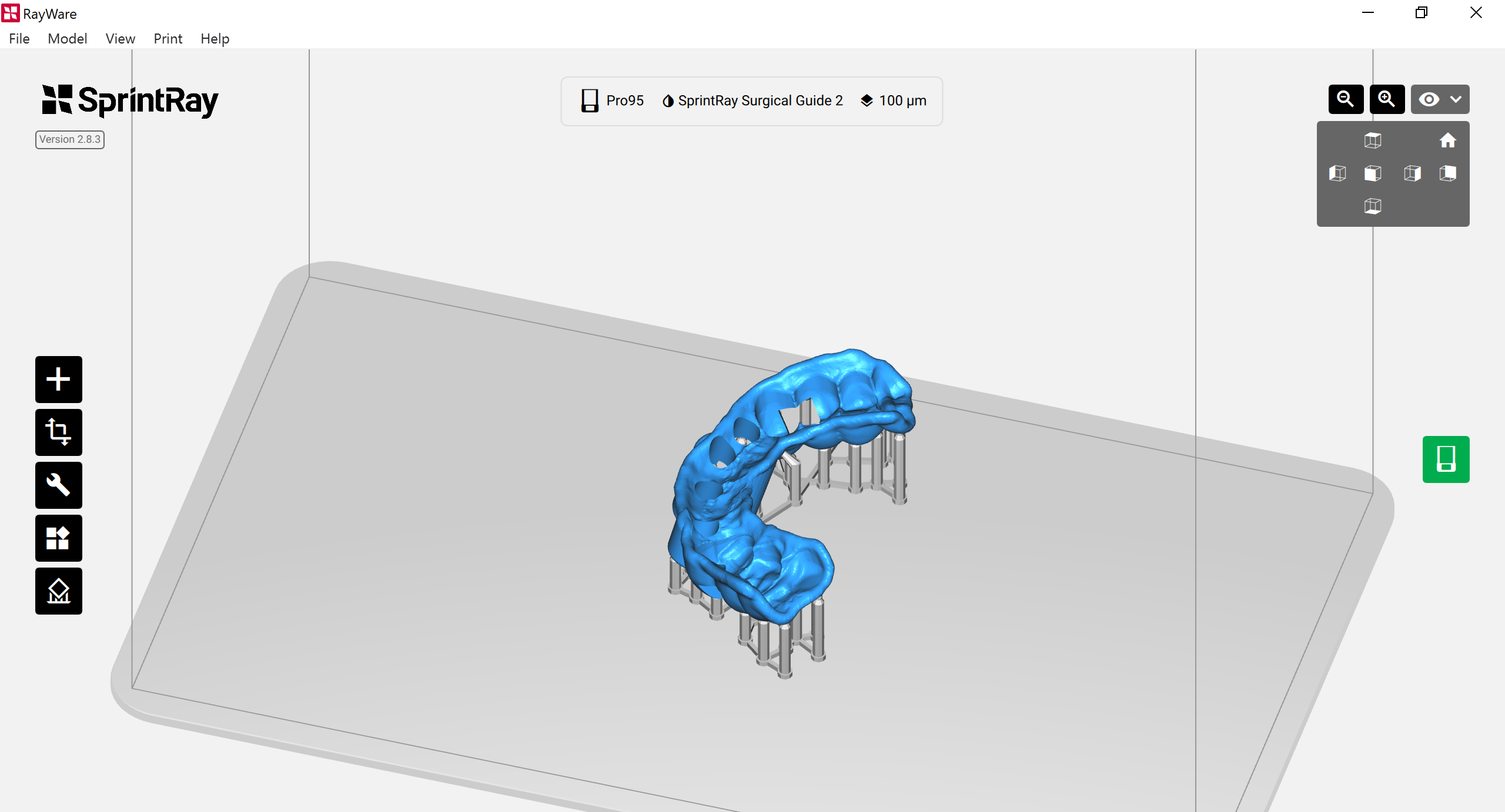
3.5.2. Print Button
In RayWare, click on the “Print” button to send the design to the printer for printing or place it in the queue to print later.
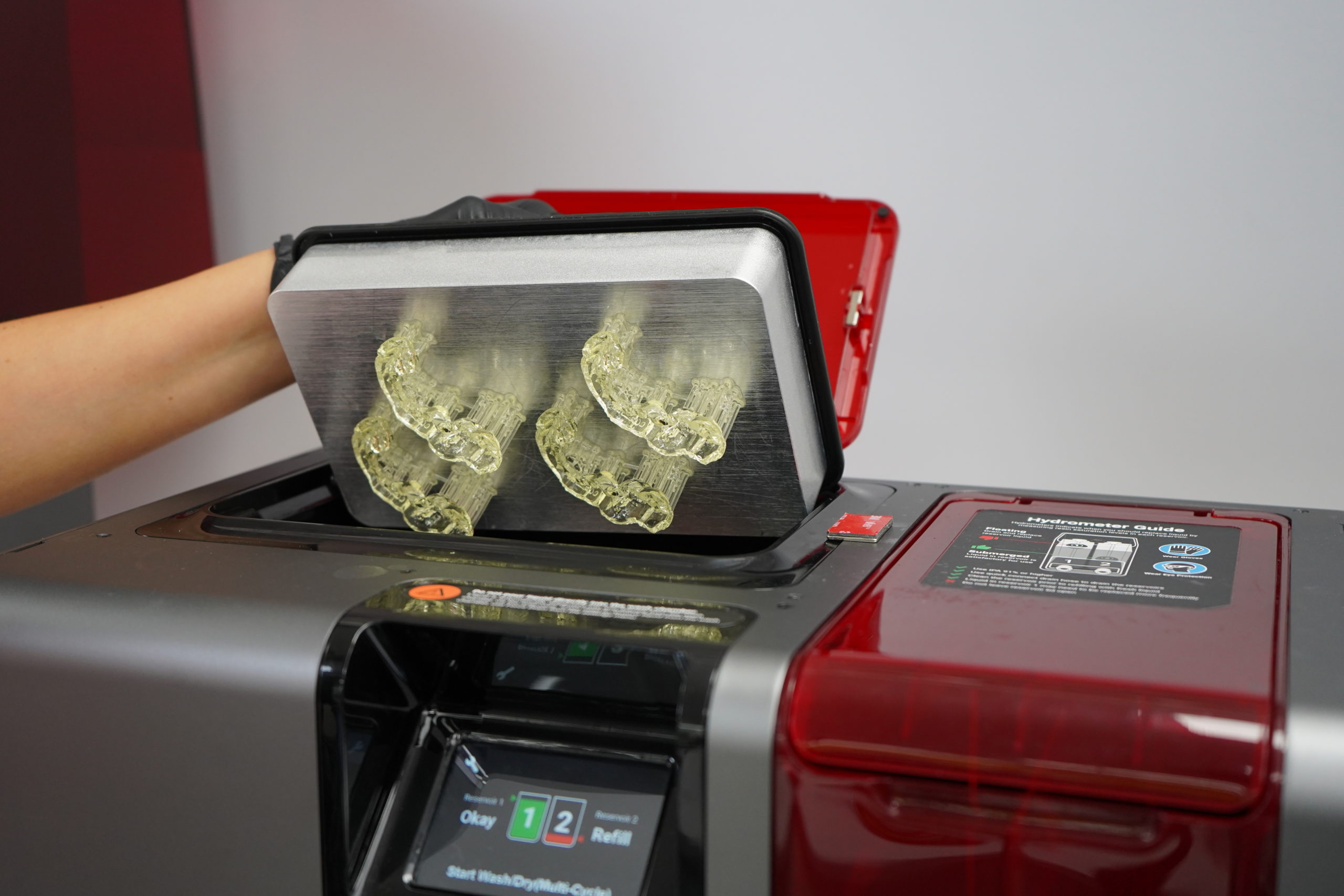

3.6. Cleaning the Surgical Guide
Once the printing is done, the Surgical Guide needs to be cleaned from the remaining liquid resin and then dried. ProWash/Dry is designed to provide the best cleaning experience in the shortest time with the lowest IPA usage.
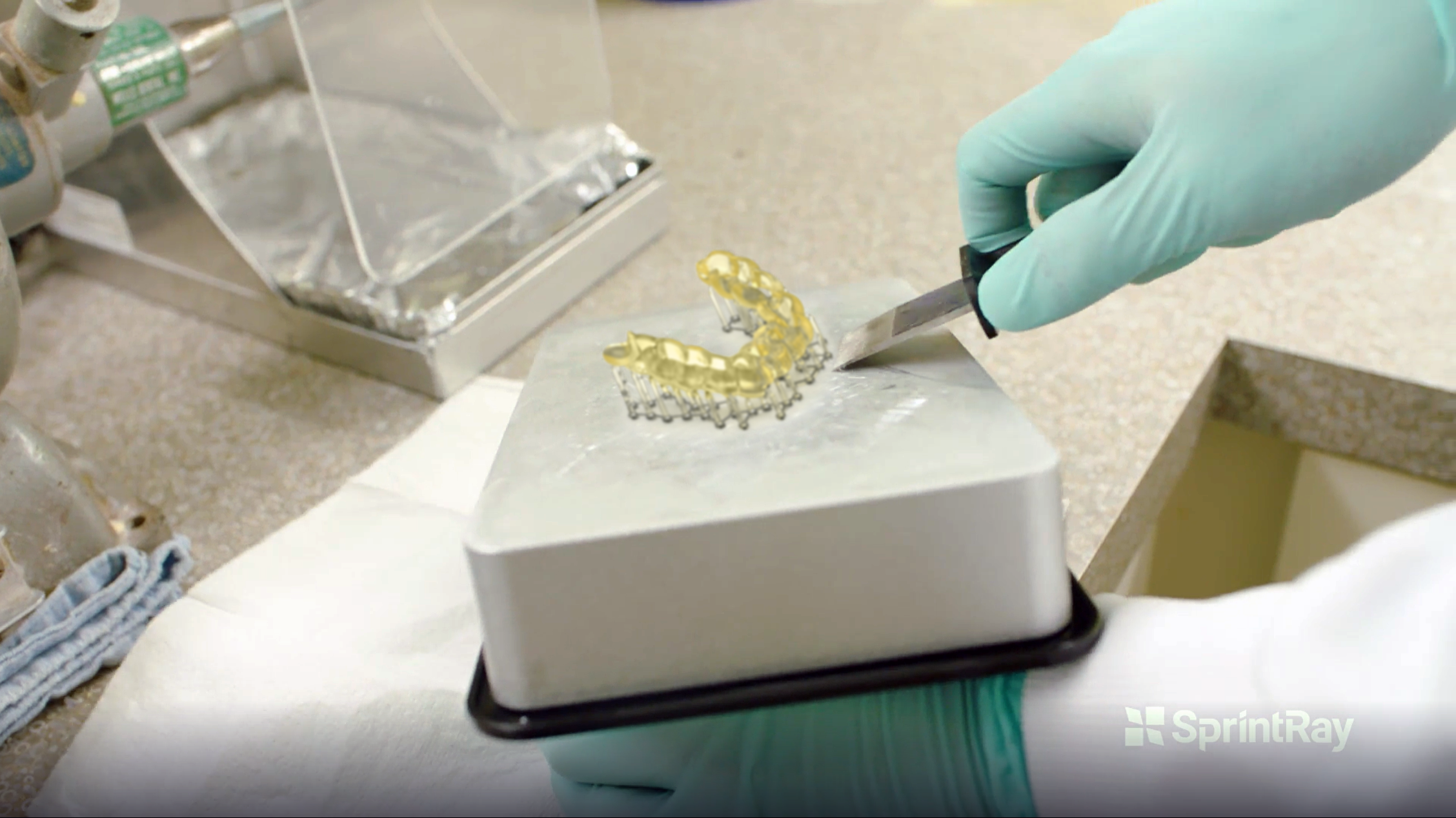
3.7. Removing Surgical Guide
Once the 3D printed Surgical Guide is cleaned and dried, please remove it from the print platform using the Part-Removal-Tool by pressing it firmly underneath the supports and gently twisting it from side to side while pushing forward. Before attempting to remove the printed Surgical Guide, make sure the platform is rested on a flat surface (table/countertop).

3.8. Post-Curing the Printed Surgical Guide
The 3D printed Surgical Guide must be properly cured to the resin manufacturer’s specifications before use. This will help obtain the complete curing as well as the best mechanical properties and accuracy. Since this is a very important step, ProCure is preset with all the settings according to the resin’s specification regarding time and temperature.
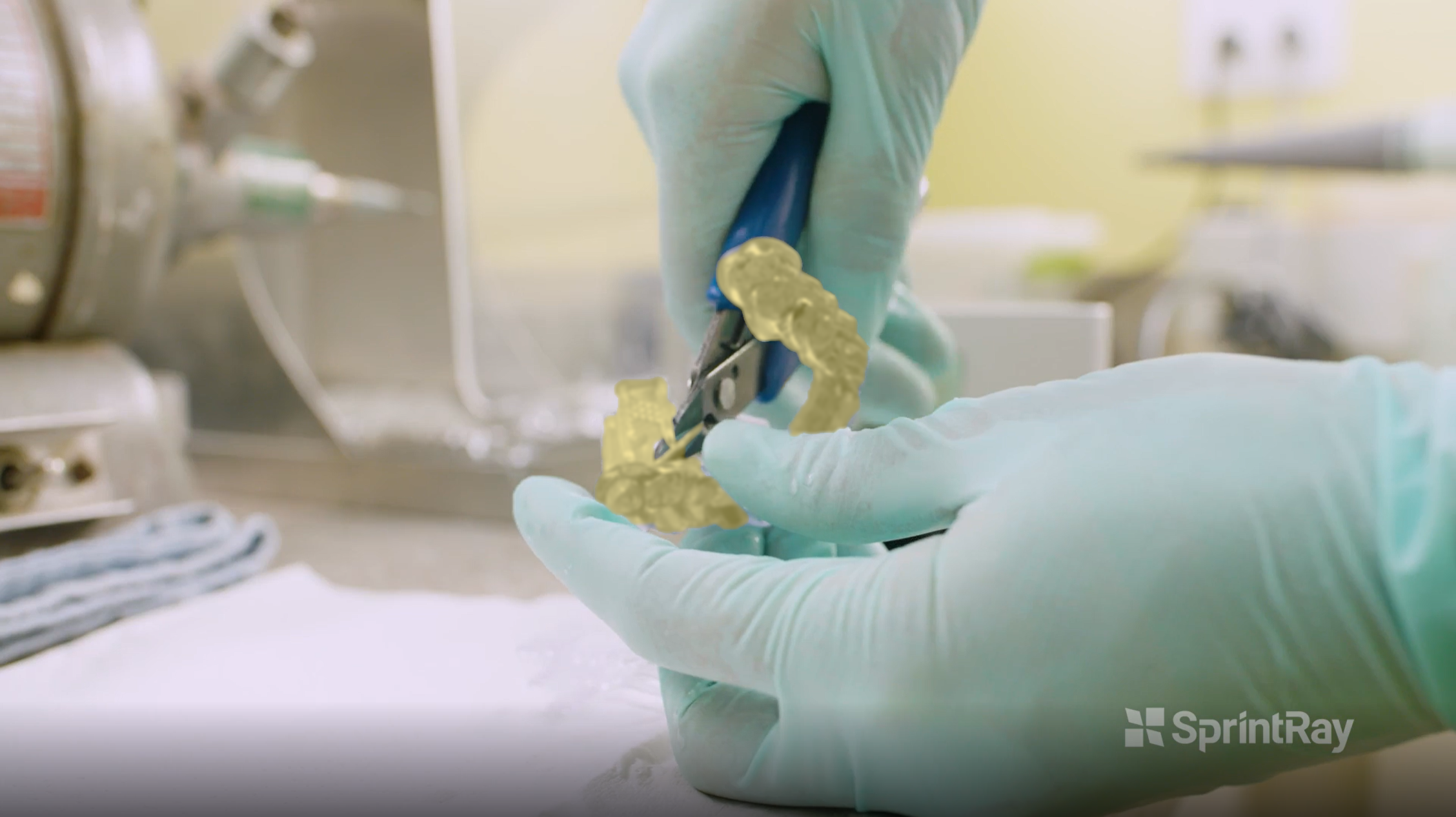

3.9. Support Removal
Once the post curing is completed, we need to remove all the supports by using a flush cutter. Try to cut as close as possible to the appliance surface to minimize the smoothening and polishing procedure.
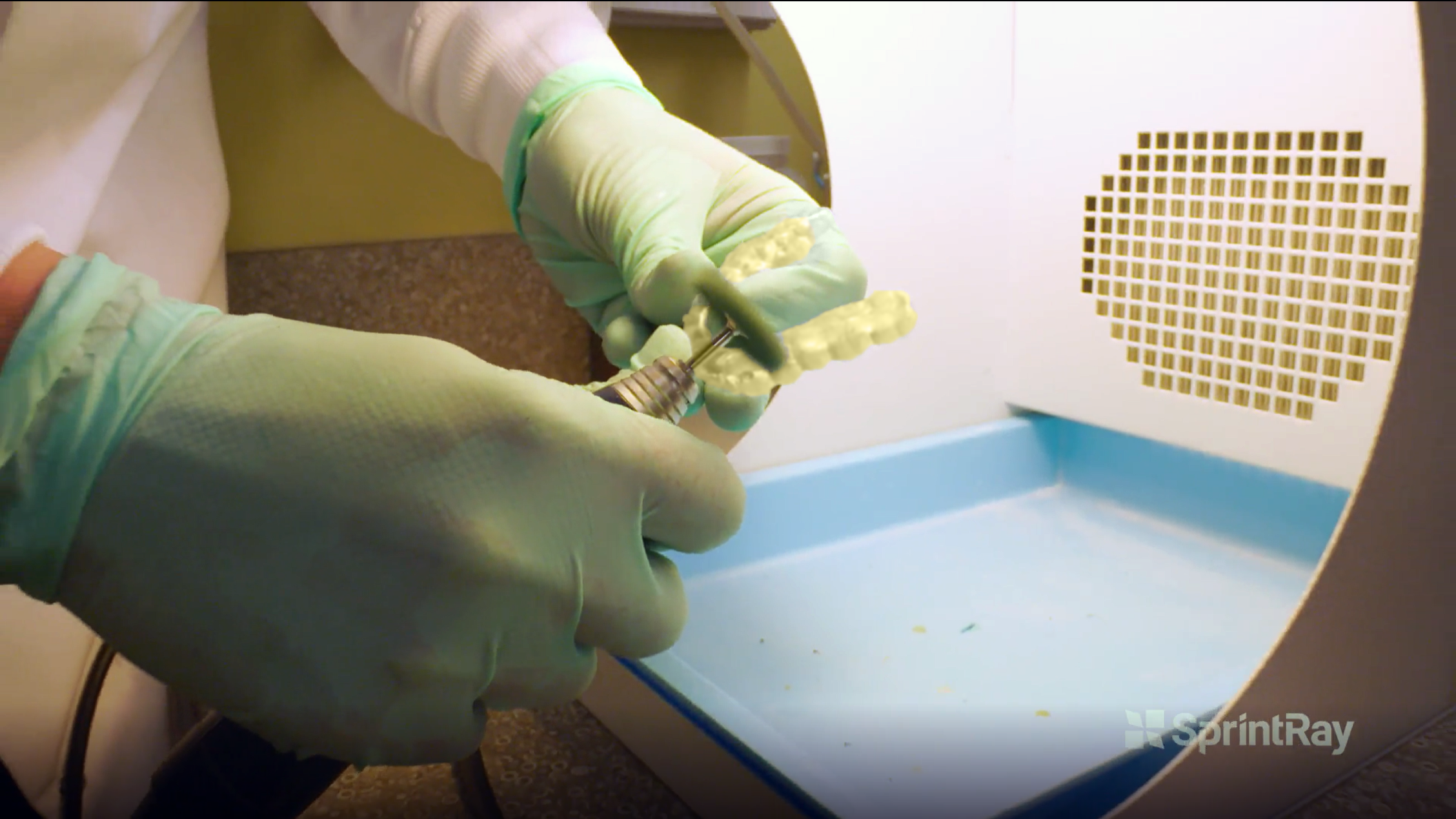

3.10. Smooth the Surgical Guide
At this step, we use a fine Scotch-BriteTM/ FuzziesTM polishing wheel to grind down the remaining knobs from the support-removal step (3.9) and smooth out the surface of the appliance. The polishing wheels are used at a low speed (about 10,000 to 12,000 rpm).
Pro Tips
- Use protective eyewear and nitrile gloves at all times to avoid eye/skin contact with uncured resin.
- Always keep the printer door closed to avoid premature curing of the resin.
- You may use a lab pearl-shaped carbide bur to smooth out the knobs if any of them fall in a depth/antagonist intersection.
- Always shake the resin bottle well before pouring into the resin tank.
- Always remove the print platform before removing the resin tank to avoid excess resin dripping inside your printer.
- ProCure may need to warm up for a few minutes before the UV lights start to shine.
- Visit https://sprintray.com/software/ to download the latest version of RayWare.
Assembly and Sterilization
The last step in this workflow prepares the printed Surgical Guide for surgery. At this step, we want to make sure the surgical guide is polished, the sleeve is assembled properly on Surgical Guide, and fully sterilized. Below, we will show you the steps involved in Polishing, Assembly, and Sterilization.
Time required: 10 minutes
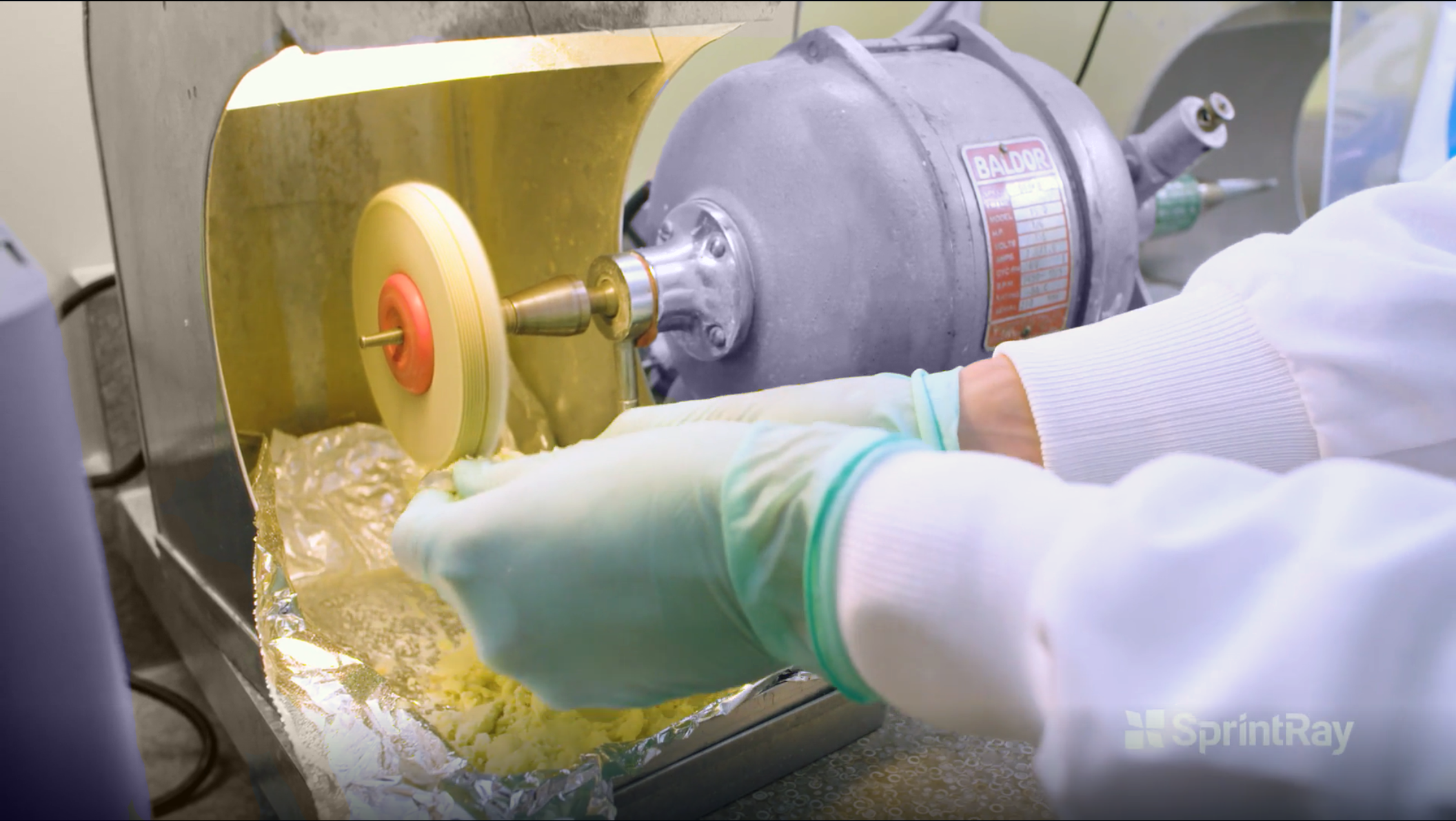

4.1. Polishing
Use a muslin polishing wheel and pumice, with a firm and consistent pressure, to reach all the appliance areas. Make sure the wheel and pumice are damp enough and the pumice is flowable.
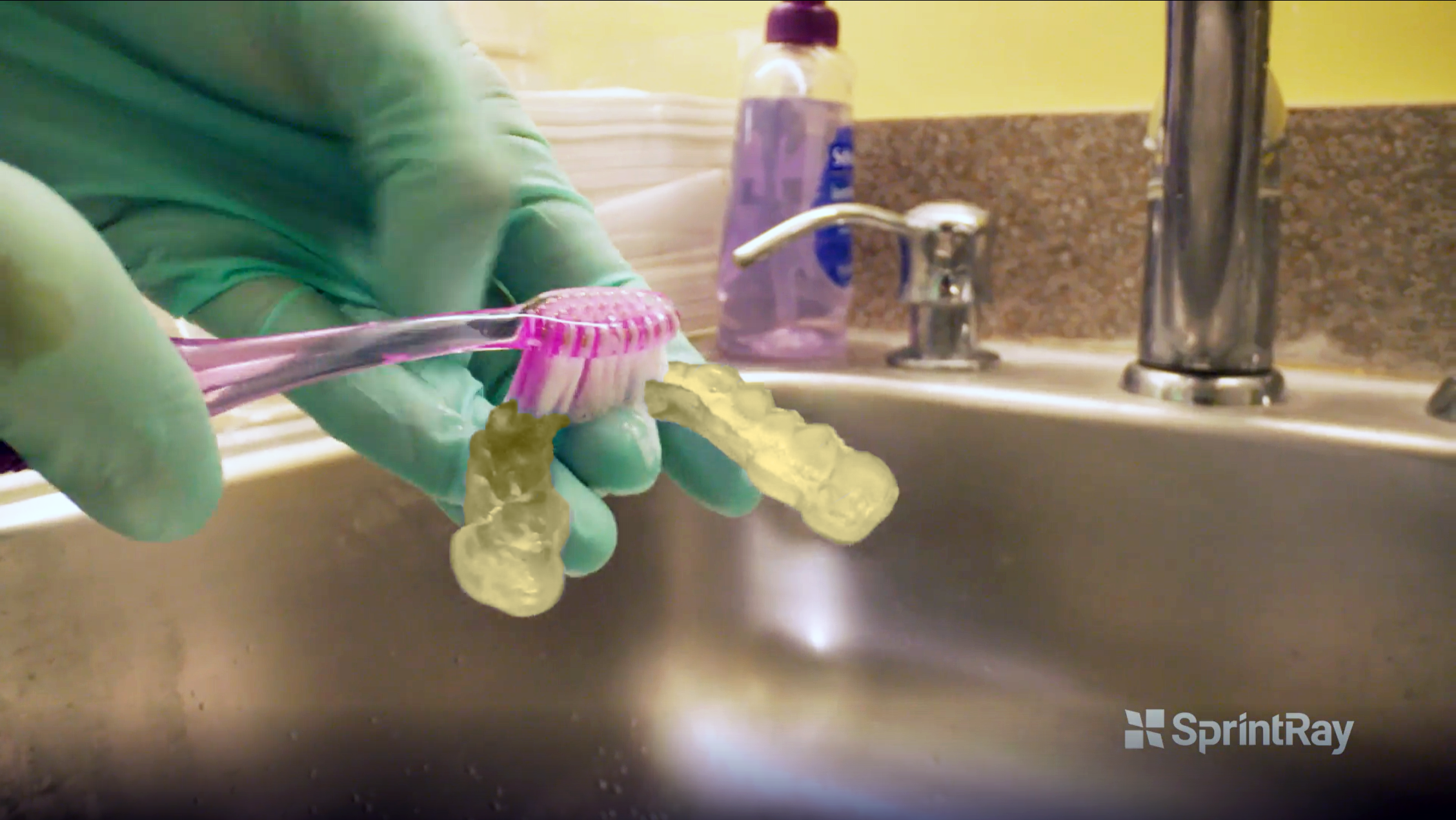
4.2. Cleaning and disinfecting the Surgical Guide
Use dish soap and a soft toothbrush to clean the appliance before assembly.
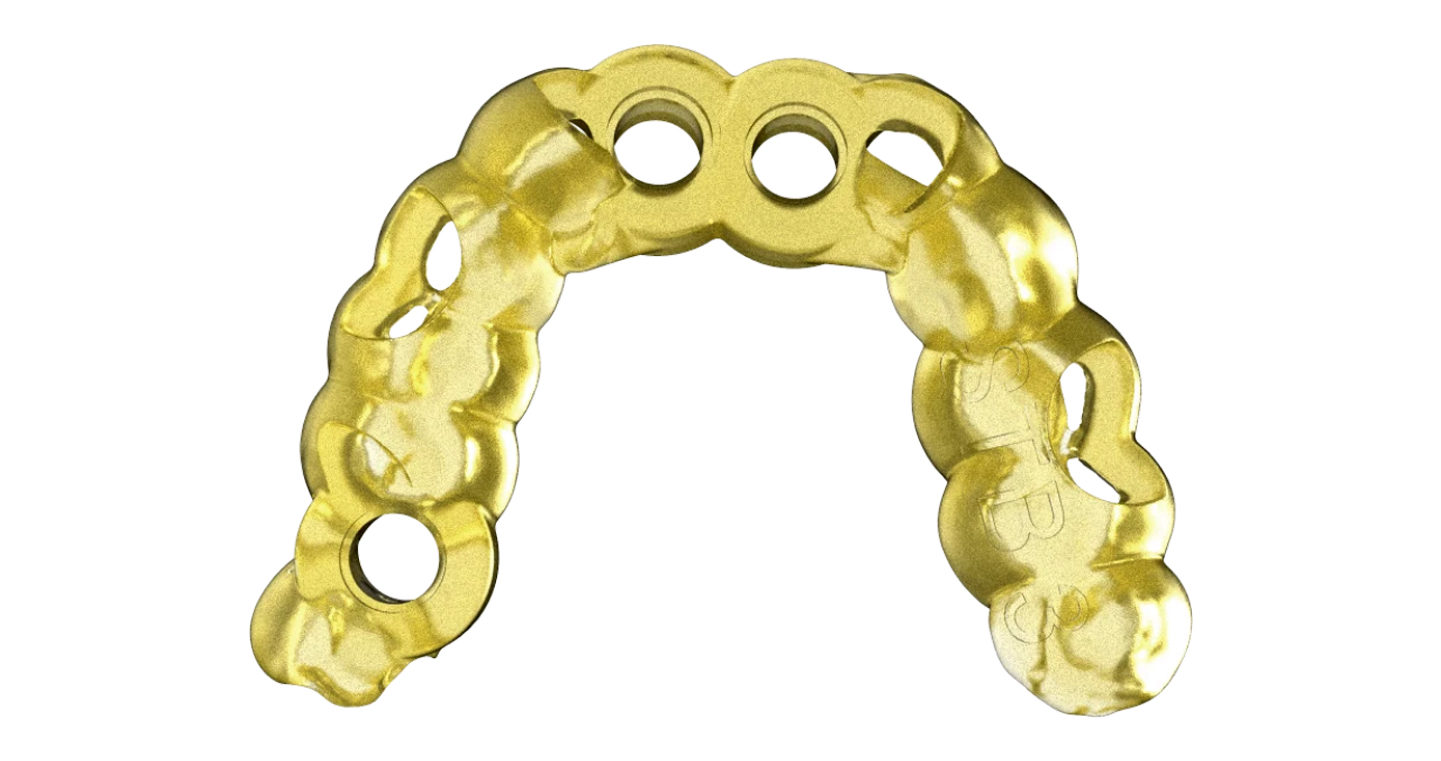

4.3. Assembling the Surgical Guide sleeve
The Surgical Guide sleeve helps avoid any damage to the surgical guide. A Surgical Guide sleeve is fitted into the corresponding surgical guide drill hole. Make sure to select a proper and compatible sleeve at the time of treatment submission.

4.4. Sterilization
The Surgical Guide is then autoclaved at 134o for 5 minutes. You may use a sterilization pouch for sterilization. If disinfection is required, use non-chemical products. If this is not possible, IPA solution is recommended for 5 minutes to disinfect.
Pro Tips
- Use protective eyewear at all times to avoid eye injuries.
- Make sure the Surgical Guide is completely dried after sterilization.
- Do not expose the Surgical Guide to excess heat or time during sterilization.
- If soaked in IPA to disinfect, do not exceed more than 10 minutes.
For further information or any questions, please contact our Customer Support team from Monday through Friday, 7AM - 5PM PST at (800) 914 8004, or visit www.support.sprintray.com.